Routing plays a crucial role in the world of web development, allowing seamless navigation between various pages or views within an application. In this blog post, we will explore Qwik’s routing capabilities with a visual guide.
Getting started
While Qwik primarily focuses on the Component API, the routing feature is supported by Qwik City. Qwik City can be thought of as the equivalent of Next.js for React, Nuxt for Vue, SvelteKit for Svelte, and Analog for Angular.
To begin, follow these commands in the terminal to create and run a new Qwik City project:
📖 Select “Empty App” as your starter template when creating the app.
npm create qwik@latest
cd qwik-app
npm startOpen the project in your preferred code editor.
Routing conventions
Qwik City employs a directory-based routing mechanism, where URL paths in the browser are determined by files and folders in the codebase. Following conventions is crucial for proper routing functionality. Let's discuss and understand the different conventions.
📖 In this blog post, we will concentrate solely on pages (UI) within Qwik City's routes, without delving into endpoints (API requests). Endpoints will be addressed comprehensively in a separate blog post.
Root route
At the heart of Qwik City’s routing is the routes folder within the src folder. To create a route for the root URL (localhost:5173), follow these steps:
- Inside the
routesfolder, create anindex.tsxfile. This file is special to Qwik City and represents the route. - Define a simple Qwik component in the
index.tsxfile, to represent the Home page:
// routes/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>Welcome home!</h1>
})Luckily for us, the starter ships with a root route. Open your browser and navigate to localhost:5173 to display the “Welcome home” message.
Visual representation
Adding more routes
Let's now create two more routes: one for the About page and another for the Profile page.
- Create a
src/routes/aboutfolder. - Inside the
aboutfolder, create anindex.tsxfile. This file represents the route. - Define a minimal Qwik component in
index.tsxfile to represent the About page:
// routes/about/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>About me</h1>
})- Similarly, create a
src/routes/profilefolder. - Inside the
profilefolder, create anindex.tsxfile. This file represents the route. - Define a simple Qwik component in the
index.tsxfile to represent the "Profile" page:
// routes/profile/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>My profile</h1>
})When you visit the root URL, localhost:5173, the home page will still be displayed. However, if you navigate to localhost:5173/about, you will see the About me page. Similarly, changing the URL to /profile will render the My profile page.
This demonstrates that routes are associated with a file based on the containing folder's name within the routes folder. The index.tsx file within the about folder corresponds to /about, while the index.tsx file within the profile folder corresponds to /profile.
Visual representation
Handling non-matching routes
What happens if you enter a URL that cannot map to a file within the routes folder? For example, /dashboard. Qwik City will automatically respond with a 404 Not Found response and a view displaying possible routes in the app in dev mode. You don't have to explicitly handle non-matching routes, as Qwik City takes care of this for you.
📖 You can also define a custom 404 page or a dynamic 404 page.
Nested routes
In addition to basic routes, Qwik City offers support for nested routes, so you can establish a hierarchical structure within your application. Let’s aim to render a page when the user navigates to the URL localhost:5173/blog. Furthermore, we need to render pages for localhost:5173/blog/first and localhost:5173/blog/second.
To implement nested routes, follow these steps:
- Create a
src/routes/blogfolder. - Inside the
blogfolder, create anindex.tsxfile for the main blog page:
// routes/blog/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>My blog</h1>
})- Navigate to
localhost:5173/blogto see the My blog page. - To implement
/blog/firstand/blog/secondroutes, createindex.tsxfiles in thesrc/routes/blog/firstandsrc/routes/blog/secondfolders:
// routes/blog/first/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>First blog post</h1>
})// routes/blog/second/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>Second blog post</h1>
})Now, navigating to localhost:5173/blog/first displays the first blog post, and localhost:5173/blog/second shows the second blog post.
By creating a nested folder structure, Qwik City automatically routes the files accordingly. This simplifies the process of creating nested routes and enhances the organization and structure of your application.
Visual representation
Dynamic routes
Predefined paths like /blog/first and /blog/second may not always be suitable for complex applications with hundreds of routes. Qwik City supports dynamic routes to handle such scenarios. Let’s create dynamic routes to handle a product listing and detail page.
To create dynamic routes, follow these steps:
- Create a
src/routes/productsfolder. - Inside the
productsfolder, create anindex.tsxfile to display a list of three products:
// routes/products/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return (
<>
<h1>Product List</h1>
<h2>Product 1</h2>
<h2>Product 2</h2>
<h2>Product 3</h2>
</>
);
});- By navigating to
localhost:5173/productsin the browser, the list of products displays. - For the details page, within the
productsfolder, create a new folder named[productId]. The square brackets indicate a dynamic route segment. - Inside the
[productId]folder, create anindex.tsxfile:
// routes/products/[productId]/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>Details about the product</h1>
});Now, when you navigate to localhost:5173/products/1, you'll get the product details page. Similarly, accessing /products/2, /products/3, or even /products/100 will display the same details page. [productId] is the dynamic route segment that can accommodate values like 1, 2, 3, and so on.
To display the specific product ID, you can make use of the useLocation() function from Qwik City. Modify the component as follows:
// routes/products/[productId]/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
import { useLocation } from '@builder.io/qwik-city';
export default component$(() => {
const loc = useLocation();
return <h1>Details about product {loc.params.productId}</h1>
});Now, when you navigate to localhost:5173/products/1, the details about product 1 display. Similarly, visiting /products/100 displays details about product 100.
Dynamic routes are beneficial when implementing the list-detail pattern in any UI application. By understanding how to create dynamic routes in Qwik City, you can build flexible and scalable applications that adapt to varying user interactions.
Visual representation
Nested dynamic routes
In the previous section, we learned about dynamic routes. Now, let's take it a step further and explore nested dynamic routes.
Complex applications often require multiple dynamic route segments. For instance, when navigating to /products/1, the user expects to get the details for product 1. Similarly, visiting /products/1/reviews/1 should display the first review for that product. Let's go over how we can achieve this.
To create nested dynamic routes, follow these steps:
- Create a
src/routes/products/[productId]/reviewsfolder. This structure takes us to the route "/products/productId/reviews." However, we also need a dynamicreviewId. - Within the
reviewsfolder, create a new folder named[reviewId]. Once again, the square brackets indicate a dynamic route segment. - Inside the
[reviewId]folder, create aindex.tsxfile where we'll define a Qwik component to display both theproductIdand thereviewId.
// routes/products/[productId]/reviews/[reviewId]/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
import { useLocation } from '@builder.io/qwik-city';
export default component$(() => {
const loc = useLocation();
const { productId, reviewId } = loc.params
return <h1>Review {reviewId} for product {productId}</h1>
});Now, if we navigate to localhost:5173/products/1/reviews/1 in the browser, the expected text displays. Similarly, navigating to productId 100 and reviewId 5 will reflect the corresponding IDs in the UI.
The key takeaway from this section is that it is possible to create nested dynamic routes by having dynamic segments in the folder names.
Visual representation
Catch-all routes
Qwik City provides the catch-all routes feature which allows for flexible routing. Let's say we want to create a documentation site with multiple features and concepts, where each concept has its own unique route. Instead of creating separate files for each route, we can use a catch-all route.
To implement a catch-all route, follow these steps:
- Create a
src/routes/docsfolder. - Inside the
docsfolder, create a folder with a special name recognized by Qwik City. Use square brackets and three dots (for example,[...slug]) to enclose a name of your choice. - Inside the
slugfolder, create anindex.tsxfile with a basic Qwik component representing the documentation home page.
// routes/docs/[...slug]/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <h1>Docs home page</h1>
});By using this structure, the index.tsx file will match any URL that contains the /docs segment in the path. This way, we can define a single file that handles all the route segments in the URL.
To access the different segments in the URL, rely on the useLocation() function that Qwik City provides. For example: localhost:5173/docs/routing/catch-all-segments can render the following component:
// routes/docs/[...slug]/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
import { useLocation } from '@builder.io/qwik-city';
export default component$(() => {
const loc = useLocation()
const slugArr = loc.params.slug.split('/')
if (params.slug.length === 2) {
return (
<h1>
Docs for feature {params.slug[0]} and concept {params.slug[1]}
</h1>
);
} else if (params.slug.length === 1) {
return <h1>Viewing docs for feature {params.slug[0]}</h1>;
}
});With catch-all segments, you can create a hierarchical structure for your routes, allowing better organization and SEO, while reusing a single file for different variations of the URL. This approach is particularly useful for documentation websites.
Visual representation
Layouts
We’ve learned that a page represents a unique UI for a specific route. However, in many cases, we want to have a consistent layout across multiple pages in our application, such as a header at the top and a footer at the bottom. With layouts, achieving this becomes much easier and more flexible.
Layouts in Qwik City
So, what exactly are layouts? A layout in Qwik City is a UI component that is shared between multiple pages in an application. It allows us to define a common structure and appearance for a group of pages, reducing redundancy and promoting code reusability.
Creating a layout
To create a layout, we need to define a Qwik component that exports as the default from a file named layout.tsx. This component should render a Slot component, which will be populated with the content of the child page during rendering.
This way, the child page becomes a part of the layout, and we can design a consistent UI around it.
Visual representation
With an empty Qwik app, a special layout file, layout.tsx is automatically generated in the routes folder.
// routes/layout.tsx
import { component$, Slot } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return <Slot />;
});The layout component contains a Slot, which represents the child page component rendered within the layout. For http://localhost:5173/about, Slot is replaced by the component defined in routes/about/index.tsx file.
Here’s the same layout with a Header and Footer component:
// routes/layout.tsx
import { component$, Slot } from '@builder.io/qwik';
import Header from '~/component/header/header';
import Footer from '~/components/footer/footer';
export default component$(() => {
return (
<>
<Header />
<main>
<Slot />
</main>
<Footer />
</>
);
});The header and footer can be customized according to our needs, providing the desired layout structure and styles. It's important to note that since the layout is applied to every page, the header and footer will be visible regardless of the current route. This means that if we navigate to different pages like /about or /products, the header and footer sections remain consistent.
Visual representation
Nested layouts
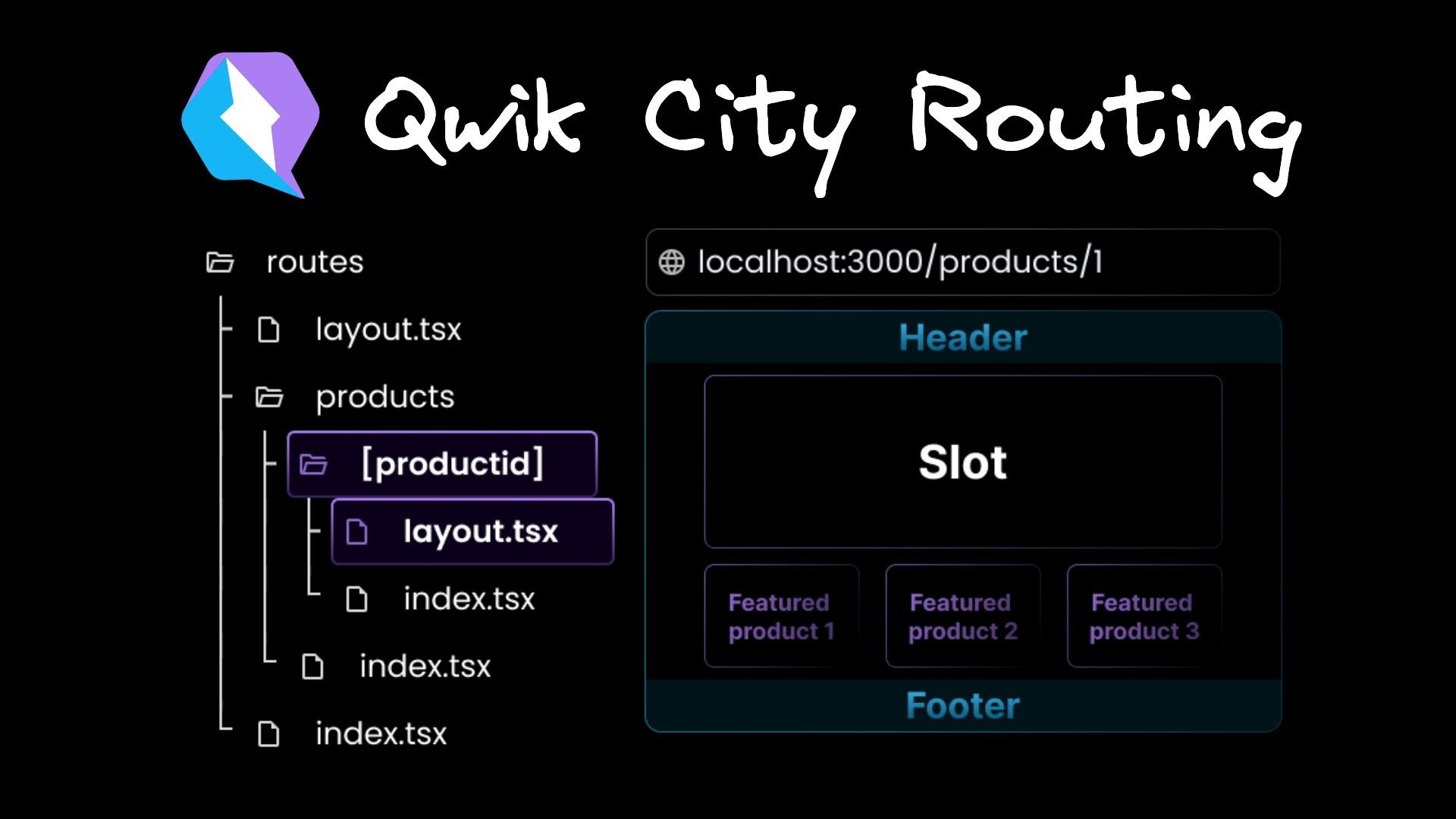
In addition to the Root layout, Qwik City supports the concept of nested layouts. This feature allows us to define layouts specific to certain areas of our application.
Consider a product details page that dynamically reads the product ID from the route parameters. Here is the folder structure for the dynamic route:
The routes folder contains a layout file and a products folder. The products folder, in turn, contains the dynamic [productId] folder.
The index.tsx file in the [productId] folder contains the ProductDetails component. This component displays the product ID in the JSX.
// routes/products/[productId]/index.tsx
import { component$ } from '@builder.io/qwik';
import { useLocation } from '@builder.io/qwik-city';
export default component$(() => {
const loc = useLocation();
return <h1>Details about product {loc.params.productId}</h1>
});If we want to create a layout specifically for the product details page, we can create a separate layout.tsx file within the [productId] folder. The nested layout file can have its own structure and content, tailored specifically to enhance the display of product details pages. Here’s the code for the product details layout file:
// routes/products/[productId]/layout.tsx
import { component$, Slot } from '@builder.io/qwik';
export default component$(() => {
return (
<>
<Slot />
<h2>Featured products</h2>
{/* Carousel of featured products */}
</>
);
});We define the nested layout as a Qwik component, similar to the Root layout, and it should also accept a Slot component. In this case, the Slot component represents the content of the product details page. As part of the layout, we render a carousel of featured products.
By nesting layouts, we can create a hierarchy of shared UI components that apply only to specific areas of our application. For instance, the Root layout can contain the main structure, such as the header and footer, while the nested layout within the productId folder can focus on displaying featured products related to that specific product.
Visual representation
Grouped layouts
Grouped layouts allow logical grouping of routes that share a layout without impacting the URL structure. They can be created by wrapping a folder in parentheses: (folderName).
For instance, routes/(auth)/register/index.tsx, routes/(auth)/login/index.tsx, and routes/(auth)/reset/index.tsx can be accessed at /register, /login, and /reset, respectively. All three routes will use the layout defined in routes/(auth)/layout.tsx.
Visual representation
Named layouts
In certain cases, sibling routes may require distinct layouts that differ significantly from one another. Qwik City provides the ability to define multiple layouts for sibling routes, including a default layout and additional named layouts. This allows child routes to request a specific named layout based on their requirements.
To create a named layout, the filename should start with "layout" followed by a dash "-" and a unique name. For example, a named layout could be named layout-two.tsx. A route can then request the named layout by adding the suffix “@two” to the file name: routes/(auth)/reset/[email protected].
Visual representation
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored the basics of routing in Qwik City. We discussed routing conventions, created routes for different scenarios, and highlighted Qwik City's convention over configuration approach for routing.
Layouts allow us to define consistent UI structures across multiple pages, reduce code duplication, and easily manage shared components. Nested layouts take this concept even further, enabling us to create specialized layouts for different sections of our application. Grouped layouts, on the other hand, allow us to share UI without affecting the URL. Named layouts allow us to select a layout for a specific route.
With Qwik City, you can easily define and manage routes by leveraging the file and folder structure of your codebase, eliminating the need for additional routing configuration.